CMA 20 Microdialysis Probes
NEW! CMA 20 PROBE WITH 30 MM MEMBRANE LENGTH
Designed for dialysis experiments in moving soft tissues such as muscle, heart, skin and adipose tissue, as well as in blood, vitreous fluid of the eye, etc.
- Tailored for dialysis in peripheral tissues and blood vessels
- Inlet and outlet tubing is attached
- Soft, non-metallic construction
- Available membranes: PAES, 20 kDa MWCO or PES, 100 kDa MWCO
- Membrane lengths: 4, 10 and 30 mm
NEW! CMA 20 PROBE WITH 30 MM MEMBRANE LENGTH
The CMA 20 Microdialysis Probe is designed for dialysis experiments in moving soft tissues such as muscle, heart, skin and adipose tissue, as well as in blood, vitreous fluid of the eye, etc.
As with the other models, the probe is of concentric construction, but is made completely from plastic materials. Due to its flexibility, the probe must be implanted in the tissue with the help of a steel needle and a split tubing.
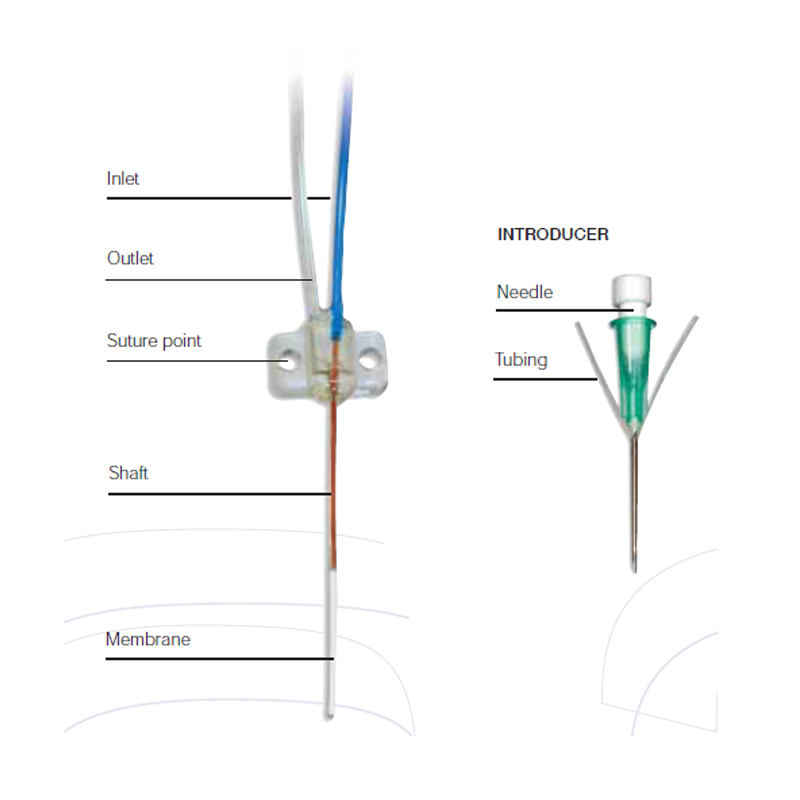
| Probe Name | CMA 20 Elite | CMA 20 High Cut-off | |||
| Membrane Length | 4, 10 and 30 mm | 4, 10 and 30 mm | |||
| Membrane Diameter | 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm | |||
| Membrane Material | PAES | PES | |||
| Molecular Weight Cut Off | 20 kDa | 100 kDa | |||
| Polyurethane Shaft Diameter | 0.77 mm | 0.77 mm | |||
| Probe Length (Shaft + Membrane) | 24 mm (20 mm Shaft + 4 mm Memb.) 24 mm (14 mm Shaft + 10 mm Memb.) 44 mm (14 mm Shaft + 30 mm Memb.) |
< | 24 mm (20 mm Shaft + 4 mm Memb.) 24 mm (14 mm Shaft + 10 mm Memb.) 44 mm (14 mm Shaft + 30 mm Memb.) |
||
| Inlet Internal Volume | 1.4 µL (4 mm Memb.) 1.4 µL (10 mm Memb.) 2.4 µL (30 mm Memb.) |
1.4 µL (4 mm Memb.) 1.4 µL (10 mm Memb.) 2.4 µL (30 mm Memb.) |
|||
| 200 mm Inlet Tubing (Blue) Membrane | 3.6 µL (ID 0.15 mm) | 3.6 µL (ID 0.15 mm) | |||
| 200 mm Outlet Tubing (Transp.) Membrane | 3.6 µL (ID 0.15 mm) | 3.6 µL (ID 0.15 mm) |
Selected Recent Publications
Zhang, X., Wang, L., et al., 2017. Online microdialysis-ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for comparative pharmacokinetic investigation on iridoids from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis in rats with different progressions of type 2 diabetic complications. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 140, pp.146–154.
Klucher, J., 2017. Enzyme kinetics studies to guide mathematical modeling of microdialysis sampling to predict in situ biochemistry. Chemistry & Biochemistry Undergraduate Honors Theses. Available at: http://scholarworks.uark.edu/chbcuht/22.
Torres, B.G.S. et al., 2017. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling as a Tool to Characterize the Decrease in Ciprofloxacin free Interstitial Levels Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Lung Infection in Wistar Rats. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, p.AAC.02553-16.
Tang, Z. et al., 2017. Liver, blood microdialysate and plasma pharmacokinetics of matrine following transdermal or intravenous administration. Die Pharmazie - An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 72(3), pp.167–170.
Su, C.-K., Tseng, P.-J., et al., 2017. Sequential enzymatic derivatization coupled with online microdialysis sampling for simultaneous profiling of mouse tumor extracellular hydrogen peroxide, lactate, and glucose. Analytica Chimica Acta, 956, pp.24–31.
Su, C.-K., Chen, Y.-T. & Sun, Y.-C., 2017. Using on-line solid phase extraction for in vivo speciation of diffusible ferrous and ferric iron in living rat brain extracellular fluid. Analytica Chimica Acta, 953, pp.87–94.
Bernardi, P.M., Barreto, F. & Dalla Costa, T., 2017. Application of a LC–MS/MS method for evaluating lung penetration of tobramycin in rats by microdialysis. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 134, pp.340–345.
Fong, S.Y.K. et al., 2017. A novel microdialysis-dissolution/permeation system for testing oral dosage forms: A proof-of-concept study. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 96, pp.154–163.
Demand, D., Schack-Kirchner, H. & Lang, F., 2017. Assessment of diffusive phosphate supply in soils by microdialysis. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 180(2), pp.220–230.
Post, E.H. et al., 2017. Changes in kidney perfusion and renal cortex metabolism in septic shock: an experimental study. Journal of Surgical Research, 207, pp.145–154.
Visit our Publications page for a complete listing of CMA 20 publications.